Avail
Key Takeaways
- Avail is a blockchain solution that provides a fast and secure data and consensus layer for building trust-minimized applications, rollups, and blockchain applications.
- Avail's data availability sampling approach helps prevent excessive strain on any one node in the network, making it a scalable and efficient solution for building trust-minimized applications, rollups, and blockchain applications.
- The various use cases of Avail, including Validiums, Sovereign Rollups, and app-specific chains, offer developers a high degree of control and flexibility in customizing their blockchain environment to their specific needs.
1. Overview
Avail is a blockchain solution that provides a fast and secure data and consensus layer for building trust-minimized applications, rollups, and blockchain applications. It is a scalable, general-purpose blockchain focused on data availability, and can be used for standalone chains, sidechains, and off-chain scaling solutions.
Chains created using Polygon SDK, Cosmos SDK, or Substrate can benefit from using Avail for this purpose. Layer-2 solutions like Validiums can also increase scalability throughput by using Avail as an off-chain data availability layer.
2. Data Availability
2.1 Technology
2.1.1 Data Availability Sampling
Data availability sampling (DAS) is a method of verifying the availability of data within a block without having to download the entire block. This helps prevent excessive strain on any one node in the network. Each node, including non-staking nodes, downloads a small, randomly selected portion of the total data. Light nodes can download small, random chunks of the full state data and use the samples to verify the availability of the full data set. The chance of incorrectly assuming full data availability after downloading N random chunks is very low.
There are two main solutions to the data availability problem: modifying on-chain data storage or storing data off-chain. Storing data on a data availability blockchain is usually cheaper on average when there is less competition for blockspace.
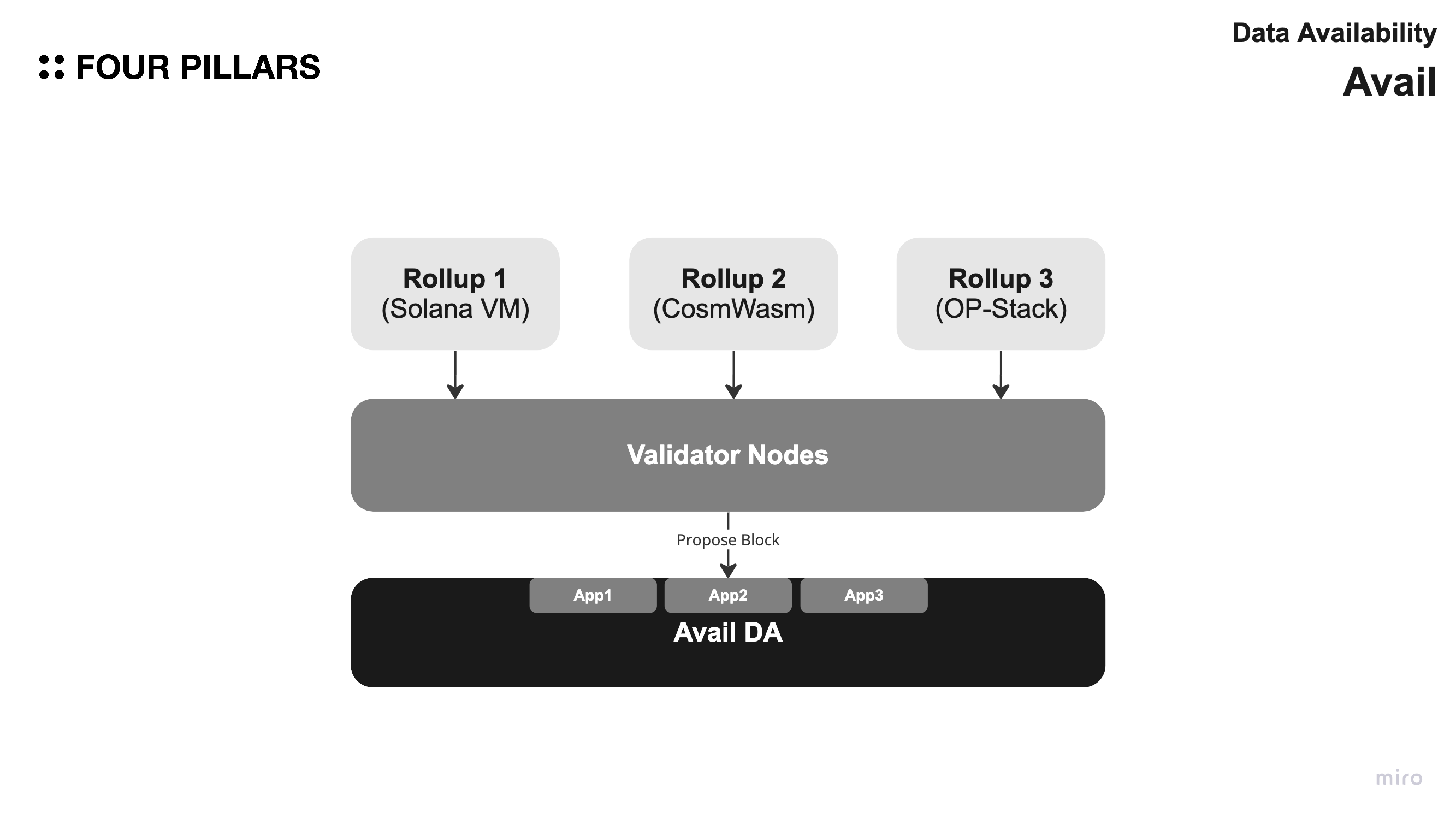
2.2.2 Application IDs
Avail is a versatile foundational layer that can support multiple modular chains at the same time, providing consensus and data availability to each of them. Headers in Avail have an index that helps a specific modular chain, also known as an "application" in Avail's context, locate and download only those block segments that are relevant to that particular application.
This operational model offers several significant advantages:
- Modular applications experience minimal interference from other activities on the base layer.
- Despite block sizes increasing, applications do not have to retrieve more data. They only need to download relevant block segments, not the entire block.
- The entire block undergoes Data Availability Sampling (DAS), where clients randomly sample tiny portions of the block to confirm data availability.
Avail offers a fast and secure data and consensus layer that provides everything you need to launch a sustainable blockchain. Avail's innovative security approach makes it easy for light clients to verify data availability through sampling over a peer-to-peer network.
2.2 Architecture
Avail blockchain network has three types of nodes which include Light clients, Full nodes, and Validator nodes.
Light clients are nodes that enable user interaction without storing the entire blockchain history. They rely on trusted nodes, known as light client infrastructure, to provide necessary data for effective network interaction.
Full nodes store the current state of the blockchain, including the latest block and transaction data. These nodes are designed to provide fast and efficient access to the current blockchain data and are optimized for rapid data access.
Validator nodes, on the other hand, are Full nodes that have a staked amount on the chain. They are responsible for producing blocks and validating the chain's functionality to maintain the network's integrity and security. Understanding the functionalities of these nodes provides a deeper insight into how Avail and blockchain networks operate, contributing to their robustness, efficiency, and scalability.
(Source: Types of Nodes | Avail Docs)
3. Use Cases
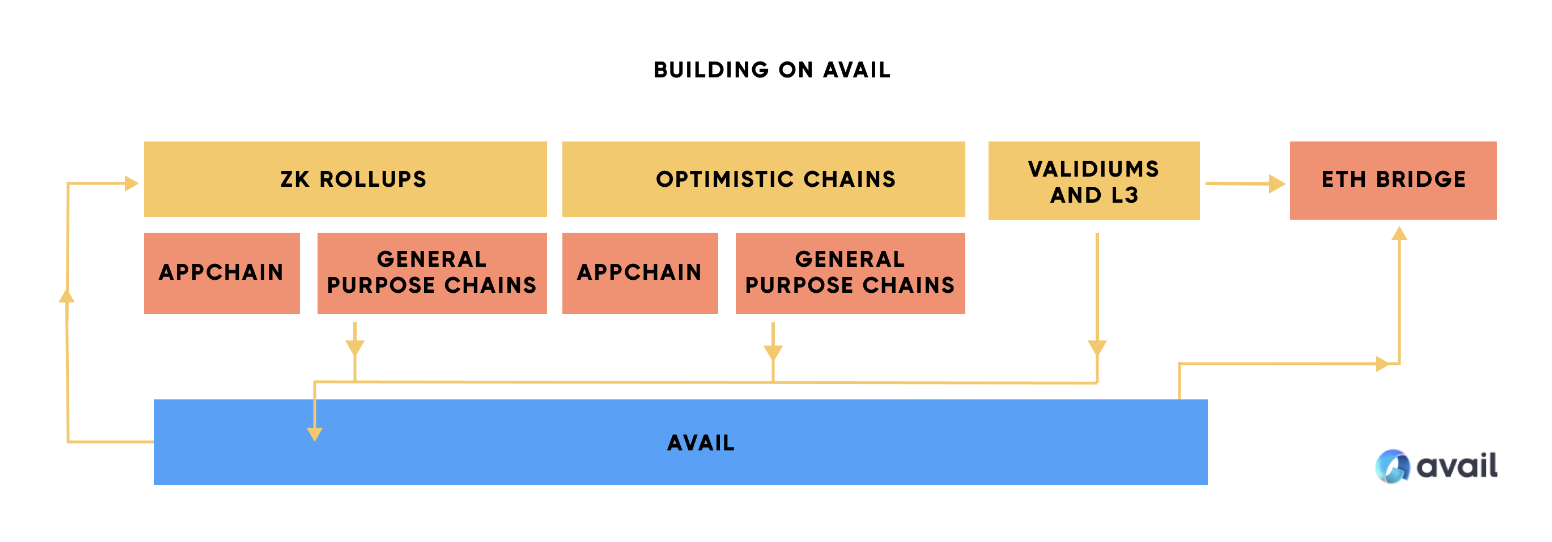
(Source: The Avail Vision: Reshaping the Blockchain Landscape)
Avail for Data Availability can be utilized by various types of blockchains. Here are some examples:
- Validiums: a type of Layer 2 rollup that sends transaction data to Avail. One noteworthy feature is that it can save up to 90% of gas fees compared to rollups that send data directly to Ethereum. This significant reduction in costs makes Validiums a cost-effective option for certain applications.
- Sovereign Rollups: another beneficial application of Avail. This technology allows you to create a blockchain in just minutes, instead of months. One significant advantage is the ability to update the logic on your chain without needing to redeploy a smart contract. Furthermore, Sovereign Rollups can interoperate with any other rollups on Avail, offering a higher degree of flexibility.
- App-specific Chains: provide the ultimate level of control over your state and execution environment. With Avail, you can create application-specific chains according to your specific requirements. This capability gives developers a tremendous amount of control and freedom to customize their blockchain environment to their specific needs.
3.3 opEVM
Rethinking Rollups with OpEVM: An Open-Source SDK to Build Optimistic Rollups
3.2 Sovereign Labs
https://github.com/availproject/avail-sovereign-da-adapter
Sovereign Labs Alpha Release Marks the First Step to Enable Sovereign Rollups on Avail
4. Team
- Anurag Arjun (Founder)
